With all the wildfires happening around the US this summer (2020) I finally got motivated enough to put together an air quality monitor home base station to see air quality in person, on the web and on my phone. If you has a Raspberry Pi plus a few other items you can set this up in an afternoon. I have it tuned to measure PM1.0, PM2.5, PM10, and Carbon Monoxide inside my house.
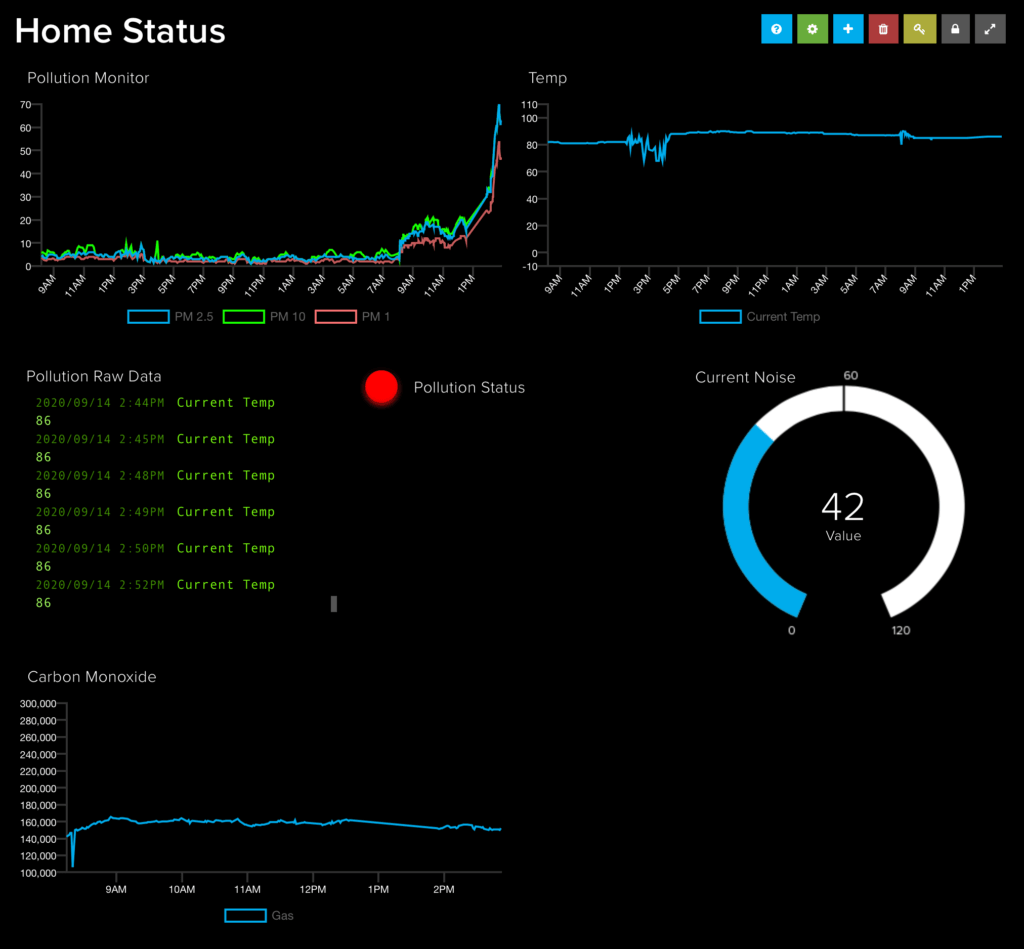
My Adafruit dashboard. I already had most of the the supplies but here is a list of what you will need:
- Raspberry Pi Zero WH
- Enviro+
- PMS50003 Particulate Matter Sensor with cable
- A free Adafruit IO account
Once you get it all plugged into, the Enviro+ into the Pi, and the PMS5003 into the Enviropi you can get the OS setup with a standard install.
I’ll assume you know how to get Raspberry setup on your PI as well as SSH into it. If not there are a great number of tutorials out there.
Once you are SSHed in, you can follow along with the instructions on the Pimoroni site or just run this script after an apt upgrade and apt update
git clone https://github.com/pimoroni/enviroplus-python
cd enviroplus-python
sudo ./install.shThis will install all the various code and samples to get playing with the sensors. The Enviro+ has a bunch of different sensors and LCDs in one making it extremely easy.

LCD
The LCD displays PM10, PM2.5 and PM1, temp, and noise level on the screen by default. If the pollution spikes, or the gas spikes the LCD will turn red and display a warning.
Adafruit IO
All the LCD data plus Carbon Monoxide, CPU Temp, and CPU load so that I just have a view that everything is healthy on the Pi.
If using install with: pip3 install adafruit-io

IFTTT
Push alerts to high pollution or gas to my phone so I can be notified immediately if something is at issue.
Key Code Snippets
Get the CPU Temp
def cpu_report_func():
# Get CPU Info
cpu = CPUTemperature()
aio.send('cpu-temp', round(cpu.temperature * 1.8 + 32))
aio.send('cpu', psutil.cpu_percent())Get CPU temp, convert to F and send both temp and usage to Adafruit
Get Noise
def noise_func():
# Get Noise
global noise_amount, noise_display
noise_amount = noise.get_amplitude_at_frequency_range(20, 8000)
noise_display = str(int(round(noise_amount * 100))) + " db"
aio.send('noise', int(round(noise_amount * 100)))Get noise within a wide range, round it and send off to display and Adafruit
Get Ambient Temps w/ Corrections
def temp_func():
# Read Temp, convert to F and adjust
global tempf_display
# Tuning factor for compensation. Decrease this number to adjust the
# temperature down, and increase to adjust up
factor = 0.6
cpu_temp = CPUTemperature().temperature
cpu_temps.append(cpu_temp)
avg_cpu_temp = sum(cpu_temps) / float(len(cpu_temps))
raw_temp = bme280.get_temperature()
comp_temp = raw_temp - ((avg_cpu_temp - raw_temp) / factor)
# Convert to America
tempf = round(comp_temp * 1.8 + 32)
tempf_display = "" + str(tempf) + " F"
print(tempf_display)
# Clean up Array so it doesn't overflow memory
if (len(cpu_temps) > 10):
cpu_temps.pop(0)
aio.send('temp', tempf)The thing you would think would be the easiest is actually the hardest due mainly to the fact the themometer is so close to the CPU that it’s picking up ambient heat from it. What this does (and is heavily cribbed from the Pimoroni example) is use the CPU temp as a baseline measure that fills up an array, correct for it and convert it to F. Since this “app” is basically one big loop I want to clear the array out after 10 readings or 10 minutes. That should give me enough history to get a good average and the temps I see pass the gut check.
The factor float may need to be adjusted for your specfic needs. For example if you don’t have the Pi in a Lego case, or have different airflow the factor you need to adjust it to may need to be different.
Get Gas, specfically Reducing AKA Carbon Monoxide
def gas_func():
global gas_reading, gas_average, gas_warning_amount
# Get Gas
gas_reading = gas.read_all()
gas_array.append(gas_reading.reducing)
# If the array is larger than 8 items dump the first one
if (len(gas_array) > 8):
gas_array.pop(0)
#print("Popped!")
aio.send('gas', round(gas_reading.reducing))
gas_average = (sum(gas_array) / len(gas_array))
gas_warning_amount = str(round(gas_reading.reducing))Get an average gas reading, current reading and send to Adafruit
Get Air Pollution
def pollution_func():
global pm25, pm10_display, pm25_display, pm1_display
# Read Particulate Matter
readings = pms5003.read()
pm25 = readings.pm_ug_per_m3(2.5)
pm10 = readings.pm_ug_per_m3(10)
pm1 = readings.pm_ug_per_m3(1)
# Send to Adafruit
aio.send('pollution.pm25', pm25)
aio.send('pollution.pm1', pm1)
aio.send('pollution.pm10', pm10)
# Draw on Screen
pm10_display = "PM10: " + str(pm10) + " ug/m3"
pm25_display = "PM25: " + str(pm25) + " ug/m3"
pm1_display = "PM10: " + str(pm1) + " ug/m3"Get the standard ug/m3 readings, send to Adafruit and display
Display Logic
# Display output of sensors on display
disp.set_backlight(1)
if (gas_reading.reducing > (gas_average * 1.05) and len(gas_array) == 8):
print("High Pollution Warning")
draw.rectangle((0, 0, 160, 80), (255, 0, 0))
draw.text((10, 20), warning, font=font, fill=text_colour)
draw.text((10, 40), gas_warning_amount, font=font, fill=text_colour)
elif (pm25 > 50):
draw.rectangle((0, 0, 160, 80), (255, 0, 0))
draw.text((10, 20), warning, font=font, fill=text_colour)
draw.text((10, 40), pm25_display, font=font, fill=text_colour)
else:
draw.rectangle((0, 0, 160, 80), back_colour)
draw.text((0, 0), pm10_display, font=font, fill=text_colour)
draw.text((0, 20), pm25_display, font=font, fill=text_colour)
draw.text((0, 40), pm1_display, font=font, fill=text_colour)
draw.text((0, 60), tempf_display, font=font, fill=text_colour)
draw.text((80, 60), noise_display, font=font, fill=text_colour)
disp.display(img)
time.sleep(60)This is a basic if else statement that has the following rules:
- If gas is higher than the average + 5% (indicating a spike) push an alarm to the Pi’s display
- If gas is ok, but PM2.5 pikes over 50 push an alarm to the Pi’s display
- Otherwise just show the PM numbers, Temp and Noise
As you can see it’s all pretty straightforward code in one big loop. If you just copy and paste the code following, add your Adafruit key, and do some additional setup in Adafruit IO you can have this up and running very quickly.
The Complete Code
import psutil
from gpiozero import CPUTemperature
import time
import datetime
from Adafruit_IO import Client
from bme280 import BME280
from enviroplus.noise import Noise
import colorsys
import sys
import ST7735
try:
# Transitional fix for breaking change in LTR559
from ltr559 import LTR559
ltr559 = LTR559()
except ImportError:
import ltr559
try:
from smbus2 import SMBus
except ImportError:
from smbus import SMBus
from pms5003 import PMS5003, ReadTimeoutError as pmsReadTimeoutError, SerialTimeoutError
from enviroplus import gas
from subprocess import PIPE, Popen
from PIL import Image
from PIL import ImageDraw
from PIL import ImageFont
from fonts.ttf import RobotoMedium as UserFont
from datetime import timedelta
# Initial Setup of sensors / API
bus = SMBus(1)
bme280 = BME280(i2c_dev=bus)
aio = Client('XXX', 'aio_XXX')
pms5003 = PMS5003()
noise = Noise()
# Create LCD class instance.
disp = ST7735.ST7735(
port=0,
cs=1,
dc=9,
backlight=12,
rotation=270,
spi_speed_hz=10000000
)
# Create array for averages
gas_array = []
cpu_temps = []
# Initialize display.
disp.begin()
# Width and height to calculate text position.
WIDTH = disp.width
HEIGHT = disp.height
# New canvas to draw on.
img = Image.new('RGB', (WIDTH, HEIGHT), color=(0, 0, 0))
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
# Text settings.
font_size = 20
small_font_size = 12
font = ImageFont.truetype(UserFont, font_size)
small_font = ImageFont.truetype(UserFont, small_font_size)
text_colour = (255, 255, 255)
back_colour = (0, 0, 0)
#size_x, size_y = draw.textsize(message, font)
warning = "Warning!"
# Calculate text position
#x = (WIDTH - size_x) / 2
#y = (HEIGHT / 2) - (size_y / 2)
x = 0
y = 0
def warm_func():
currentTime = datetime.datetime.now()
draw.rectangle((0, 0, 160, 80), (30, 160, 30))
draw.text((10, 20), "Warming Up", font=font, fill=text_colour)
draw.text((0, 66), currentTime.strftime("%a, %b %d %I:%M:%S %p"), font=small_font, fill=text_colour)
disp.display(img)
print("Warming Up at " + currentTime.strftime("%a, %b %d %I:%M:%S %p"))
def cpu_report_func():
# Get CPU Info
cpu = CPUTemperature()
aio.send('cpu-temp', round(cpu.temperature * 1.8 + 32))
aio.send('cpu', psutil.cpu_percent())
def noise_func():
# Get Noise
global noise_amount, noise_display
noise_amount = noise.get_amplitude_at_frequency_range(20, 8000)
noise_display = str(int(round(noise_amount * 100))) + " db"
aio.send('noise', int(round(noise_amount * 100)))
def temp_func():
# Read Temp, convert to F and adjust
global tempf_display
# Tuning factor for compensation. Decrease this number to adjust the
# temperature down, and increase to adjust up
factor = 0.6
cpu_temp = CPUTemperature().temperature
#print("CPU Temp: " + str(cpu_temp))
cpu_temps.append(cpu_temp)
avg_cpu_temp = sum(cpu_temps) / float(len(cpu_temps))
raw_temp = bme280.get_temperature()
comp_temp = raw_temp - ((avg_cpu_temp - raw_temp) / factor)
# Convert to America
tempf = round(comp_temp * 1.8 + 32)
tempf_display = "" + str(tempf) + " F"
print(tempf_display)
# Clean up Array so it doesn't overflow memory
if (len(cpu_temps) > 10):
cpu_temps.pop(0)
aio.send('temp', tempf)
def gas_func():
global gas_reading, gas_average, gas_warning_amount
# Get Gas
gas_reading = gas.read_all()
gas_array.append(gas_reading.reducing)
# If the array is larger than 8 items dump the first one
if (len(gas_array) > 8):
gas_array.pop(0)
#print("Popped!")
aio.send('gas', round(gas_reading.reducing))
gas_average = (sum(gas_array) / len(gas_array))
gas_warning_amount = str(round(gas_reading.reducing))
def pollution_func():
global pm25, pm10_display, pm25_display, pm1_display
# Read Particulate Matter
readings = pms5003.read()
pm25 = readings.pm_ug_per_m3(2.5)
pm10 = readings.pm_ug_per_m3(10)
pm1 = readings.pm_ug_per_m3(1)
# Send to Adafruit
aio.send('pollution.pm25', pm25)
aio.send('pollution.pm1', pm1)
aio.send('pollution.pm10', pm10)
# Draw on Screen
pm10_display = "PM10: " + str(pm10) + " ug/m3"
pm25_display = "PM25: " + str(pm25) + " ug/m3"
pm1_display = "PM10: " + str(pm1) + " ug/m3"
def systemup_func():
with open('/proc/uptime', 'r') as f:
uptime_seconds = float(f.readline().split()[0])
uptime_string = str(timedelta(seconds = uptime_seconds))
aio.send('system-uptime', uptime_string)
try:
# Warm Up
warm_func()
time.sleep(120)
while True:
# Run Sensor Functions
cpu_report_func()
noise_func()
gas_func()
temp_func()
pollution_func()
systemup_func()
# Display output of sensors on display
disp.set_backlight(1)
if (gas_reading.reducing > (gas_average * 1.05) and len(gas_array) == 8):
print("High Pollution Warning")
draw.rectangle((0, 0, 160, 80), (255, 0, 0))
draw.text((10, 20), warning, font=font, fill=text_colour)
draw.text((10, 40), gas_warning_amount, font=font, fill=text_colour)
elif (pm25 > 50):
draw.rectangle((0, 0, 160, 80), (255, 0, 0))
draw.text((10, 20), warning, font=font, fill=text_colour)
draw.text((10, 40), pm25_display, font=font, fill=text_colour)
else:
draw.rectangle((0, 0, 160, 80), back_colour)
draw.text((0, 0), pm10_display, font=font, fill=text_colour)
draw.text((0, 20), pm25_display, font=font, fill=text_colour)
draw.text((0, 40), pm1_display, font=font, fill=text_colour)
draw.text((0, 60), tempf_display, font=font, fill=text_colour)
draw.text((80, 60), noise_display, font=font, fill=text_colour)
disp.display(img)
time.sleep(60)
# Turn off backlight on control-c
except KeyboardInterrupt:
disp.set_backlight(0)I was going to break this all out to be a detailed how-to, but the code is pretty simple. Let me know on Twitter if you are having issues and I can reply and revised as needed.
Run the Python Program on Startup
Once you create that Python file, its just a matter of setting it up as SystemD server and you are off to the races! If you are unsure how to do that, I explain how I set it up in another blog post here.
FAQs
Some questions you may have that I hope I can answer
Why are the PM2.5 Numbers Different than the AQI I see in apps?
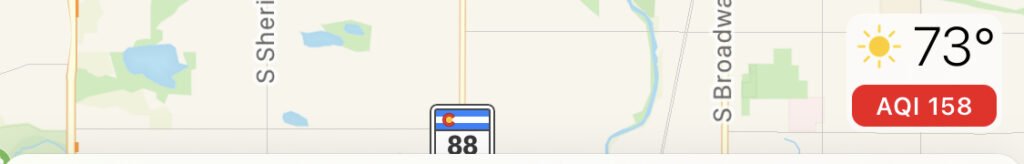
Air Quality in Denver as reported by Apple Maps It comes down to a really weird formula. The goal of which was to conform it to anything over 100 being bad. A really good writeup on the topic can be found here: https://smartairfilters.com/en/blog/difference-pm2-5-aqi-measurements/
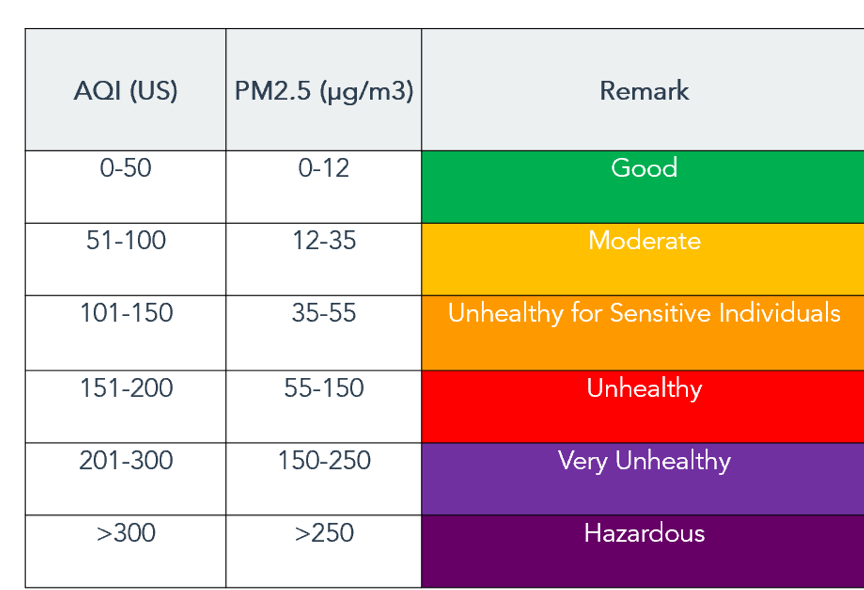
But just looking at the chart below gives you a good idea that any ug/m3 over 35 is really bad. Here is a site that does the conversion for you: PM25 Converter
My Adafruit IO isn’t getting any data
- In Adafruit you need to create the feed names, say
pm25and then in the Python code above you need to also call it the same thing, so Adafruit knows how to match up the values